Your basket is currently empty!
Pro5® MHC Class I Pentamers
Pro5® MHC Class I Pentamers
the most consistent, most published commercial
technology for detecting antigen-specific CD8+ T cells
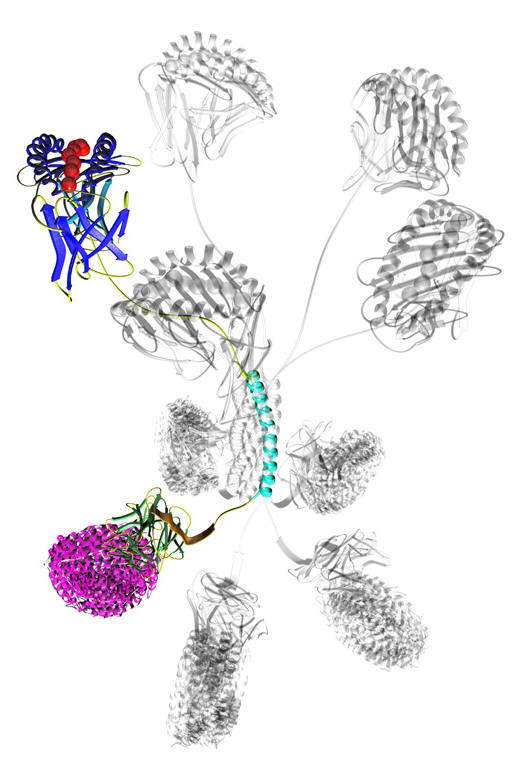
Pro5® MHC Pentamer. The beautiful rational design of Pro5® MHC Pentamers presents five MHC peptide complexes in a plane at one end of their pentameric coiled-coil core and five detection tags in a second plane at the opposite end of the core.
Pro5® Pentamers feature
- Uniform bright staining
- Flexible labelling options
- Excellent long term stability
- More than 1800 scientific publications
- Better uniform avidity than MHC tetramers
- Wide range of disease areas and catalog items
- Purified four times for best consistency
- Custom made for the peptides you require at no extra charge
- Application support from the experienced immunology team at ProImmune
Learn how your research will benefit from the use of Pro5 Pentamers:
Examples of Published Pro5® Pentamer Staining Data:
Collaborative publication by an international team in China and the UK including Oxford University and ProImmune identifying and characterizing SARS-CoV-2 specific T cell responses in convalescent patients:
Peng Y., Dong T., et al. (2020). “Broad and strong memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cells induced by SARS-CoV-2 in UK convalescent COVID-19 patients”
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41590-020-0782-6
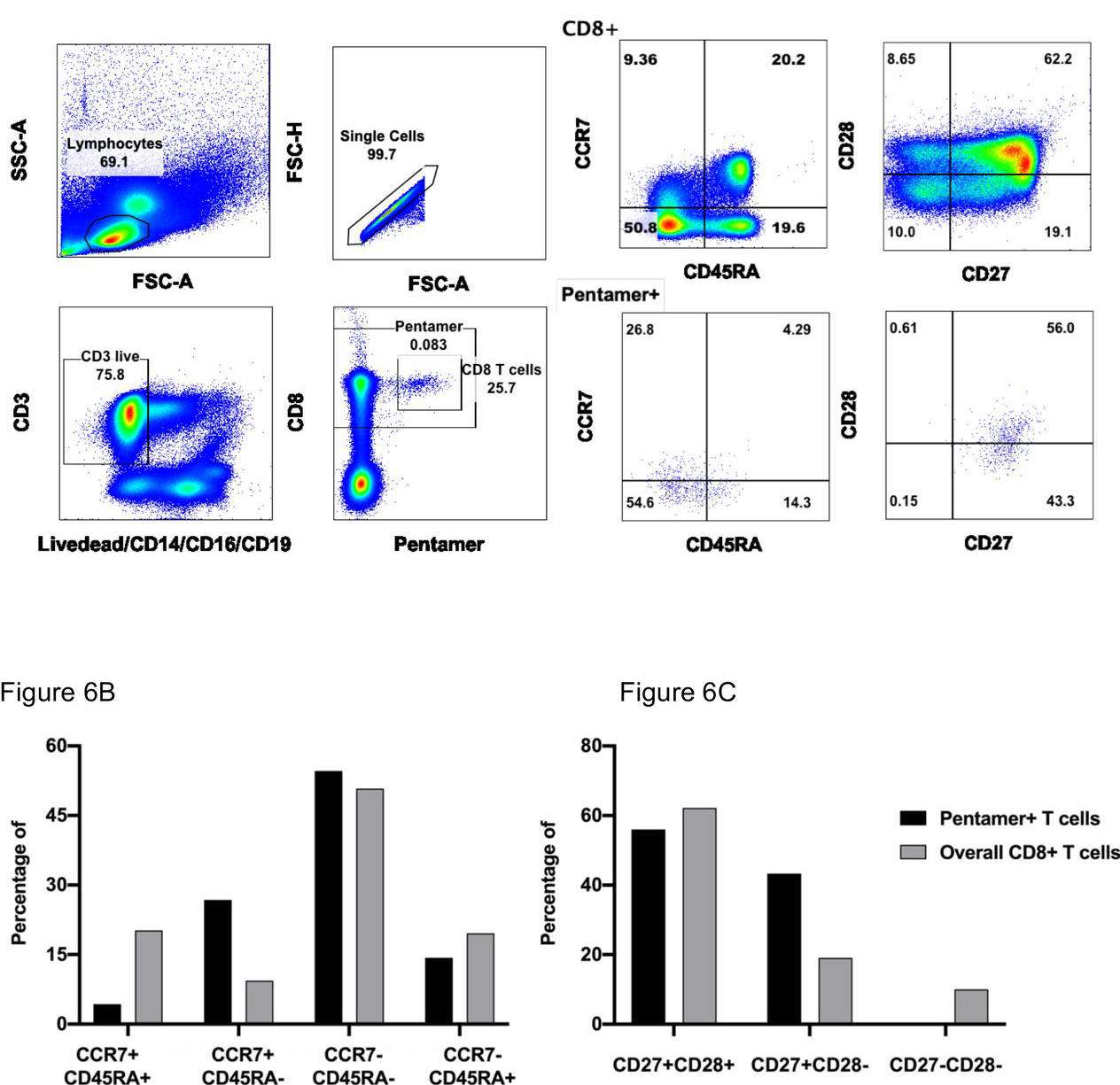
Figure 1. memory phenotype and differentiation status of HLA-B*40:01 restricted NP322-331 (MEVTPSGTWL)-specific T cells. PBMC were isolated and stained with NP/B*40:01 Pentameric complexes and markers of T cell differentiation, and analysed using flow cytometry. A) Expression of differentiation markers of CCR7 and CD45RA on CD8+ Pentamer+ T cells. B): Expression of differentiation markers of CD27 and CD28 on CD8+ Pentamer+ T cells.
In this short clip, Prof. Tao Dong (Professor of Immunology, University of Oxford) describes her latest work in antigen-specific memory T cell responses in SARS-CoV-2 patients, highlighting the recent Nature Immunology publication from her group and the use of Pro5® MHC Pentamers in their work:
For the full talk follow:https://youtu.be/AG4RaIoARC0
If you are interested in Professor Tao Dong’s work and want to hear more, follow this link to our interview with Tao about her career in T cell immunology and recent work with SARS-CoV-2: https://youtu.be/wHIjQn6wwUo
Ferdosi S. R. et. al. (2019). “Multifunctional CRISPR-Cas9 with engineered immunosilenced human T cell epitopes”
Nature Communications 10, Article number1842
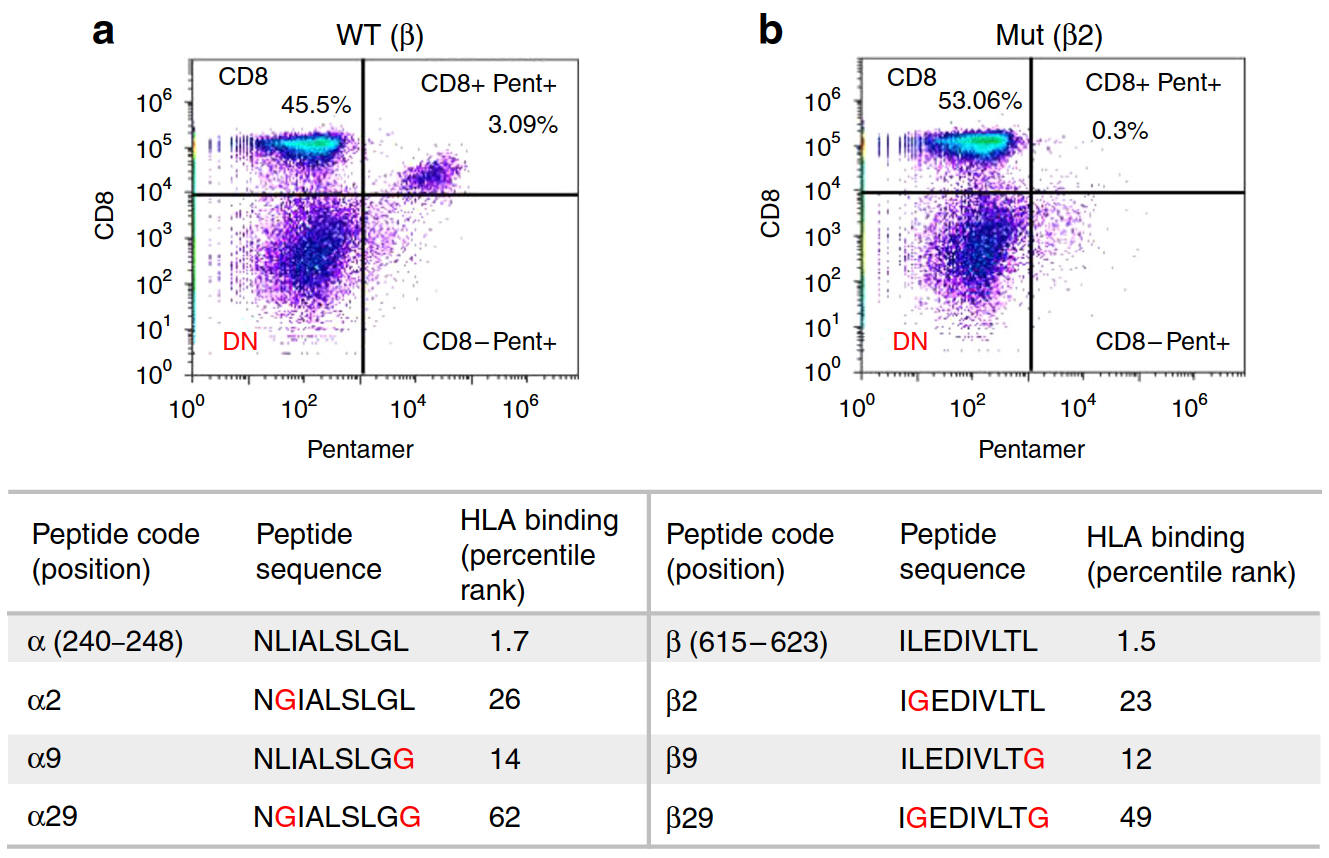
Figure 2. Pro5® Pentamer-specific SpCas9 immunodominant epitope-specific CD8+T cell recognition is abolished after anchor residue mutation. a Epitope β-specific CD8+T cell response detected using β-specific Pro5® Pentamer in PBMCs stimulated with peptide β-pulsed antigen presenting cells. b The percentage of CD8+ Pro5® Pentamerβ+T cells was reduced to 0.3% when healthy donor B cell APCs were pulsed with the mutated peptide β2. Table: Positions, sequences, and IEDB HLA binding percentile rank of epitopes α and β before and after mutation of the anchor (2nd and/or 9th) residues. Sb, normalized binding score; Si, normalized immunogenicity score.
Webb J. et. al. (2010). “Profound elevation of CD8+ T cells expressing the intraepithelial lymphocyte marker CD103 (αE/β7 Integrin) in high-grade serous ovarian cancer.”
Gynecological Oncology 2010, Volume 118, Issue 3, Pages 228–236
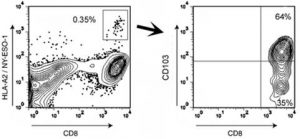
Figure 3. CD8+ T cells specific for the tumor antigen NY-ESO-1 are predominantly CD103+. Flow cytometry analysis of T cells derived from the malignant ascites of an HLA-A2+ EOC patient (IROC013) who demonstrated reactivity to an HLA-A2-restricted epitope of NY-ESO-1. The analysis shows the frequency of CD8+ lymphocytes staining positive with an A*02:01/SLLMWITQV (NY-ESO-1157–165) Pro5® Pentamer. Pentamer-positive CD8+ T cells were further characterized for CD103 expression (right panel). All events were first gated on total lymphocyte populations by forward and side scatter.
Pro5® Pentamers: consistency by design for the most demanding applications
When you are trying to detect a rare population of antigen specific T cells you will understand the importance of having a research tool that is sensitive, accurate and gives reproducible results. Pro5® MHC Class I Pentamers are designed for these objectives. They bind directly to T cell receptors of a particular specificity, determined by the Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) allele and peptide combination. Pro5® Pentamers can be used to detect and separate antigen-specific CD8+ T cell populations as rare as 0.02% of lymphocytes. They are also suitable for detailed epitope characterization and further immune monitoring.
Unlike MHC multimers from other sources, which can be of variable quality and stability, Pro5® Pentamers benefit from a superior design and are made to a professional standard. Each Pentamer is purified four times before being subjected to several stringent quality control steps. Using the Pentamer technology enables you to achieve accurate and reproducible results.
Key Publication
Pro5® Pentamers used in study to show HIV up-regulates checkpoint inhibition, leading to T cell exhaustion marked by TGIT
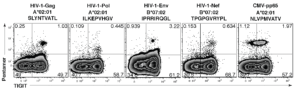
Figure 4. TIGIT expression on CD8+ terminal effector T cells and HIV-specific CD8+ T cells co-stained with various Pro5® MHC Class I Pentamers.
Chew GM et al. (2016) “TIGIT Marks Exhausted T Cells, Correlates with Disease Progression, and Serves as a Target for Immune Restoration in HIV and SIV Infection.” PLoS Pathog 12(1):e1005349. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1005349
Praise for Pro5® Pentamers
Dr Cath Bollard, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston TX, USA “Pro5® MHC Pentamers have played an important part in our study on adoptive immunotherapy for cancer and viral infections, post-transplant. We use Pentamers to detect and quantify the populations of antigen-specific T cells in CTL lines made for clinical use. We also use them to detect antigen-specific CTL in the peripheral blood of transplant patients, pre and post-CTL-infusion. The Pentamers were chosen for their stability and for the increased intensity and specificity of the positive population compared to MHC tetramers. We have found Pentamers to be consistent and reliable, and ProImmune’s customer service is excellent”.
In this short testimonial Prof. Eui-Cheol Shin (KAIST, South Korea), shares how ProImmune’s Pro5® MHC Class I Pentamer technology has enabled his research to understand the mechanism of bystander T cell activation and his recommendation of ProImmune’s Pro5® MHC Class I Pentamers:
Pro5® Pentamer Labeling Options
- Pre-labeled with R-PE, APC or biotin Pentamer Fluorotag. Choose this option for ready to go Pentamers for your application.
- Unlabelled, for labeling with R-PE, APC or biotin Pentamer Fluorotag. Choose this option for long-term storage of unlabeled pentamers, projects which require larger batch qualification, changing labels over time, or staining with Pentamer pools.
- Biotin labelled Pentamers allow for unconstrained secondary staining with, e.g. fluochrome-conjugate streptavidin of choice to address any colour or mass cytometry channel.
- Fluorochrome labeled or biotin labeled pentamers are readily usable for bead isolation and subsequent culture of antigen-specific CD8+ T cell.
Labeling Choices in Detail
 |
Directly labeled Pentamers are stored at 4°C and are quick and convenient to use. They are especially valuable in the analysis of a single donor sample for multiple peptide specificities. A single donor sample may be simultaneously stained and analyzed for multiple specificities by double or triple staining with labeled Pentamers. This generates a more complete profile of the immune response whilst reducing the total number of cells required for staining. Any combination of R-PE-labeled, APC-labeled and biotin-labeled Pentamers may be used for this purpose.Unlabeled Pentamers may be stored at -80°C and are guaranteed for 12 months under such conditions, making them perfect for long-term studies. Internal validation of a large batch of Pentamer at the beginning of a study saves time by not having to re-qualify new reagent batches every few months. Unlabeled Pentamers offer the user added staining flexibility, in that the same complex may be used with a number of different fluorochromes. This feature makes experimental design more adaptable, especially when choosing antibodies to cell surface markers or intracellular proteins that are only available in certain colors. |
Advantages of Pro5® MHC Class I Pentamers |
||
Pro5® MHC Pentamers |
MHC Tetramers |
|
| Avidity & configuration |
5 MHC-peptide complexes per Pentamer in the same orientation result in enhanced avidity interaction with T cell receptor (TCR) | MHC-peptide complex held in a tetrahedral configuration typically allowing only 3 MHC-peptide complexes to bind to TCRs |
| Brightness | Unique labeling technology allows up to 5 fluorescent labels to attach to each Pentamer, yielding brighter signal | By nature, tetramers will have one fluorescent label located at the center of the complex |
| Labeling flexibility | Biotin-labeled Pentamers and unlabeled Pentamers, which can be labeled with the fluorochrome of choice, maximize the range of possible applications | Tetramers, made by multimerizing biotinylated MHC monomers with fluorescent labeled streptavidin, must be supplied pre-labeled |
| Stability | Unlabeled Pentamers can be stored long-term at -80°C and then used when required | Tetramers incorporating a fluorochrome must be stored at 4°C, reducing their shelf life |
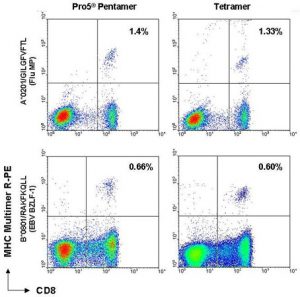
Figure 5. MHC multimer staining vs. CD8 FITC of peripheral blood (PBMC) samples. 1 x 105 PBMCs with specificity for each antigen shown were stained with either Pro5® Pentamer or MHC tetramer. The figure shows live cells and demonstrates the sensitivity and increase in mean fluorescence intensity when cells are stained with Pentamer vs. tetramer.
Further detail on Pro5® MHC Class I Pentamers and related products
Pro5® Pentamer Product Size Options
Pro5® Pentamers are available in 50, 150 and 500 test quantities. Please enquire for larger batches.
Staining Protocols for Labeled and Unlabeled Pro5® PentamersComprehensive staining protocols for Pro5® Pentamers are available in the Pro5® MHC Pentamer Handbook and on the Protocols page. |
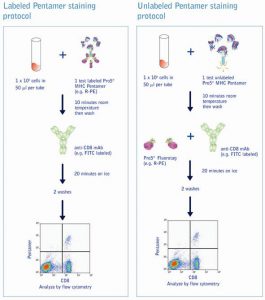
Further Pro5® MHC Class I Pentamer product options
Pro5® MHC Class I Pentamer and Anti-CD8 Kits
Pro5® Pentamer analysis should be carried out with co-staining of the CD8+ T cell population. All Pentamers are optionally available in a kit with a FITC-labeled, anti CD8 monoclonal antibody (human or mouse). The antibody clone supplied in the kit has been tested for superior performance in conjunction with Pentamer products, and is provided as a separate aliquot. This enables the user to titrate the antibody in order to find the optimum working dilution. There are over 250 different Pentamer specificities available in our catalog, encompassing epitopes for cancer and infectious diseases such as CMV, EBV, HBV, HCV, HPV, Influenza and many more List of catalog Pentamers.
Custom Pro5® MHC Class I Pentamers
If your chosen specificity is not in our range, custom Pro5® Pentamers are available in the same format as catalog items. Our technical expertise and experience making thousands of different MHC-peptide complexes means that we are able to provide custom reagents efficiently and with a high rate of success. Custom Pentamers are usually subject to a non-refundable set-up charge, which will be applied once for each item. The set-up charge will not be applied to repeat orders of the same Pentamer. The price for a custom Pentamer includes the synthesis of the specific custom peptide. ProImmune will only proceed with the synthesis of a custom Pentamer if we are confident that the peptide will bind sufficiently to the relevant MHC allele. Usually synthesis will proceed if the affinity score is 21 or higher on www.syfpeithi.com. Lower scoring peptides will be considered if sufficient supporting evidence is available for binding.
Matched Peptides
ProImmune provides matched peptides for all catalog peptide specificities and custom Pro5® Pentamers. Matched peptides are provided lyophilized in 1 or 2 mg quantity, and at a guaranteed purity of >70% (immunograde). They are suitable for in vitro T cell stimulation experiments and can be purchased at a much-reduced cost compared to a separate standard custom peptide synthesis. Matched peptides are dispatched in less than one week.
Links to further information about Pro5® MHC Class I Pentamers
List of Catalog Pro5® Pentamers
Technical Webcasts about Pro5® Pentamers
Application Support for Pro5® MHC Class I Pentamers
Co-staining with Intracellular Cytokines
Pro5® MHC Class I Pentamer Sample Product Sheets
Pro5® MHC Class I Pentamer – APC Labeled
Pro5® MHC Class I Pentamer – Biotin Labeled
Pro5® MHC Class I Pentamer – A0201 Negative Control
Pro5® MHC Class I Pentamer – R-PE Labeled
Pro5® MHC Class I Pentamer – Unlabeled
Key Publication
Team at GSK uses Pro5 Pentamers to study mRNA vaccines that can protect against several Flu strains
Magini D. et al. (2017). “Self-Amplifying mRNA Vaccines Expressing Multiple Conserved Influenza Antigens Confer Protection against Homologous and Heterosubtypic Viral Challenge.” PLOS One
http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0161193
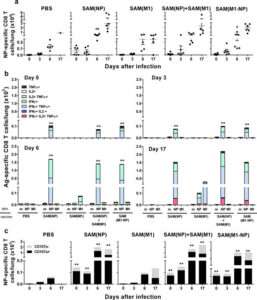
Figure 6. NP-specific CD8+ T-cell responses in lungs after influenza challenge. BALB/c mice were immunized i.m. twice, 8 weeks apart, with PBS, 0.1 μg of self-amplifying mRNA (SAM®) vectors SAM(NP), SAM(M1), SAM(M1-NP), or with 0.2 μg of SAM(NP)+SAM(M1). Four weeks after the second immunization, mice were infected with PR8 virus. NP-specific CD8 T cells recruited in the lungs after the infection were characterized by flow cytometry. (a) Numbers of NP-specific CD8+ T cells determined using Pro5® MHC Pentamers. Data are from individual mice (depicted as dots), while solid lanes indicate the mean±SD. (b) Cumulative frequency of Ag-specific, cytokine-secreting CD8+ T cells, indicated as absolute number per lung. The color code represents the different combinations of cytokine produced by the respective cells after in vitro stimulation with medium (m), NP147-155 peptide (NP), or M1 peptide pool (M1), as indicated. (c) Absolute number of NP-specific CD8+ T cells positive (black bar) or not (grey bar) for CD107a. Data derived from two independent and merged experiments. Statistical analyses were performed using the Mann-Whitney U test. *p<0.05; **p<0.01 compared to the PBS-treated group.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0161193.g006
Abbreviated abstract:
Current hemagglutinin (HA)-based seasonal influenza vaccines induce vaccine strain-specific neutralizing antibodies that usually fail to protect against mismatched circulating viruses. Inclusion of conserved proteins such as the nucleoprotein (NP) and the matrix protein 1 (M1) can increase effectiveness by eliciting cross-reactive T-cells. However, efficient priming of T-cell responses requires the right delivery system. Here we show novel self-amplifying mRNA (SAM®) vectors expressing influenza NP (SAM(NP)), M1 (SAM(M1)), and NP and M1 (SAM(M1-NP)) delivered with lipid nanoparticles (LNP) induce robust polyfunctional CD4 T helper 1 cells, while NP-containing SAM also induced cytotoxic CD8 T cells. Robust expansions of central memory (TCM) and effector memory (TEM) CD4 and CD8 T cells were also measured. An enhanced recruitment of NP-specific cytotoxic CD8 T cells was observed in the lungs of SAM(NP)-immunized mice after influenza infection that paralleled with reduced lung viral titers and pathology, and increased survival after homologous and heterosubtypic influenza challenge. We show for the first time that the co-administration of RNA (SAM(M1-NP)) and protein (monovalent inactivated influenza vaccine (MIIV)) was feasible, induced simultaneously NP-, M1- and HA-specific T cells and HA-specific neutralizing antibodies, and enhanced MIIV efficacy against a heterologous challenge.
Key Publication
Pro5® MHC Class I Pentamers used to study EBV-linked CD8+ T cell immunopathology in MS brain tissue
Serafini B. et al. (2019) ,“Epstein-Barr Virus-Specific CD8 T Cells Selectively Infiltrate the Brain in Multiple Sclerosis and Interact Locally with Virus-Infected Cells: Clue for a Virus-Driven Immunopathological Mechanism” J. Virol., Dec 19 Vol 93, Issue 24 e-00980-19
https://jvi.asm.org/content/93/24/e00980-19
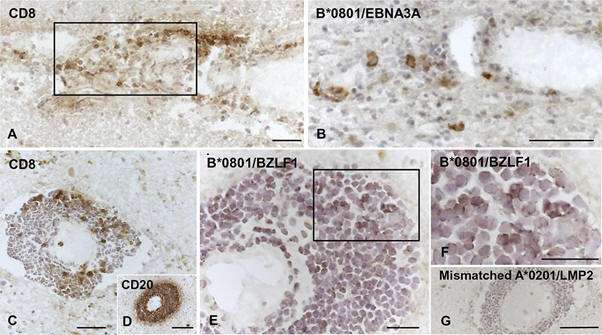
Figure 7. Visualization of EBV pentamer-binding cells in brain sections from HLA-B*0801+ MS donors. Serial brain sections from two HLA-B*0801+ MS donors were stained with MAbs to CD8 and CD20 and with EBV-peptide coupled Pro5® MHC Pentamers. (A and B, donor MS234) Perivascular cuff containing CD8 T cells (A) and some cells binding the B*0801/EBNA3A pentamer (B) in an active WM lesion. (C to G, donor MS121) Large perivascular cuff containing scattered CD8 T cells (C), tightly packed CD20 B cells (D), and several cells binding the B*0801/BZLF1 pentamer (E; panel F shows the area within the frame in panel E at high-power magnification) at the periphery of an active WM lesion; in the same cuff, no staining is observed after incubation with HLA-mismatched A*0201/LMP2 pentamer (G). Nuclei were stained with hematoxylin. Bars, 100 μm (D and G) and 50 μm (A to C, E, and F).
Abbreviated conclusions from this study:
The aim of this study was to test the hypothesis that EBV-specific CD8 T cells are involved in CNS tissue damage in MS by mediating an immunopathological response toward a persistent intracerebral EBV infection that was documented in previous studies.The key finding is that EBV-specific CD8 T cells are commonly found in the MS brain and are significantly more frequent than CMV-specific CD8 T cells, as evidenced through tissue staining with a range of EBV and CMV-specific Pro5® MHC Pentamers.Furthermore, CD8 T cells recognizing influenza A virus or a putative CNS autoantigen are not detected. These data suggest that entry of EBV-specific CD8 T cells into the MS brain results from active recruitment rather than nonspecific extravasation due to the local inflammatory process.

